Storage
Almost all computers use a storage hierarchy, which puts fast but expensive and small storage options close to the CPU and slower but less expensive and larger options further away
- Generally the fast volatile technologies (which lose data when off power) are referred to as "memory", while slower persistent technologies are referred to as "storage".
Levels
Registers (L0)
- registers hold words from cache memory
On-chip cache (L1)
- L1 cache holds cache lines retrieved from the L2 cache
- ex. SRAM
Off-chip cache (L2)
- L2 cache holds cache lines retrieved from memory
- ex. SRAM
Main memory (L3)
- Main memory holds disk blocks retrieved from local disks
- ex. DRAM
Local secondary storage (L4)
- local disks hold files retrieved from disks on remote network servers
- ex. local disk
Remote secondary storage (L5)
- ex. distributed filesystems, web servers
Storage on a CD
- the data on a CD is stored in an outward spiral pattern. The CD port on the computer has motor which rotates the CD. It also has a laser arm which follows the spiral, as the disk spins.
- the spiral track has little bumps along it. The bumps are used to encode the binary value. The laser arm in the CD port has a sensor attached to it, which "listens for" the reflection of the laser. If the sensor receives the light, an electrical signal is generated and sent to the microprocessor, which interprets it as a
1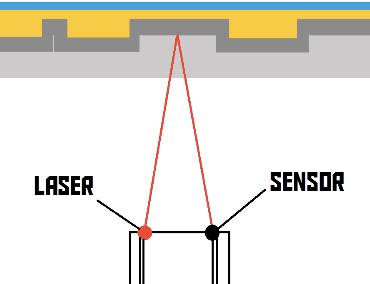
Children
Backlinks