Storage Methods
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks)
A RAID is simply multiple physical hard drives acting as a single virtual hard drive
- RAID provides redundancy across several disks attached to the same machine
The main goals of RAID are to safeguard your data with some sort of backup/failsafe, or to speed up reading/writing.
- When data is read, it is read from both hard drives and checked to make sure they agree.
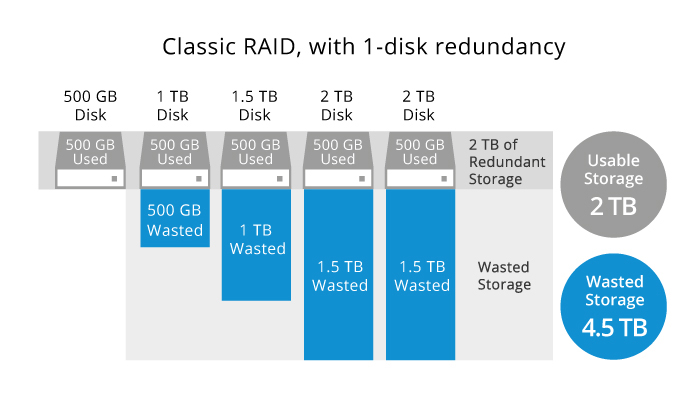
RAID bases its storage creation on the smallest drive in the storage pool. As shown in the below image, if the smallest drive in a classic RAID storage pool is 500 GB, all other drives in the storage pool can each only contribute 500 GB. As a result, the storage pool ends up with 2 TB of usable storage and 4.5 TB of wasted storage.
- note: this does not apply to SHR (Synology Hybrid Raid)
There are 3 main types (with example of storing a song):
- RAID-0 - the song is stored across multiple hard drives. Therefore, if one fails then the file is corrupted
- Least safe
- RAID-1 - all hard drives have the same data. Therefore, if one fails, the redundancy provided by the second will allow us to retain all of the data.
- RAID-1 is where disk mirroring is most commonly used
- RAID-5 - the song is stored across multiple hard drives (like RAID-0), but each hard drive will have its own backup. If one hard drive fails, the backup is restored so we don't get a corrupted file.
- This is the safest, but also more expensive and a bit slower.