API Gateway
API Gateway is a fully managed service that allows us to create, publish, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs (read: a set of endpoints) at any scale
Allows us to create 2 types of API:
- RESTful APIs
- Web APIs, that enable real-time two-way communication applications
Handles all the tasks involved in accepting and processing up to hundreds of thousands of concurrent API calls, including:
- traffic management
- CORS support
- authorization and access control
- throttling
- monitoring
- API version management
API Gateway’s REST API type allows users to setup HTTP proxy integrations, which can be used for forwarding incoming requests with different path patterns to different origin servers according to the API specifications
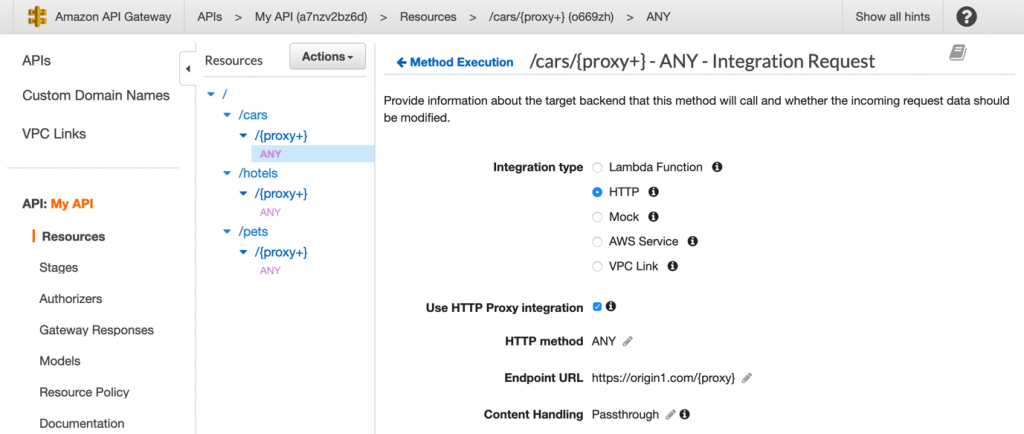
- Supports containerized and serverless workloads, as well as web applications.
- Pay for the API calls you receive and the amount of data transferred out
- API Gateway is combined well with Lambda, whereby we make an endpoint and cause the endpoint to trigger the AWS Lambda
Authorizers
Lambda Authorizers
When a client makes a request to one of your API's endpoints, API Gateway calls your Lambda authorizer, which takes the caller's identity as input and returns an IAM policy as output.
A Lambda authorizer is useful if you want to implement a custom authorization scheme that uses a bearer token authentication strategy such as OAuth or SAML, or that uses request parameters to determine the caller's identity.
There are two types of Lambda authorizers:
- token-based - the authorizer receives the caller's identity in a bearer token (e.g. JWT or OAuth)
- request parameter-based - the authorizer receives the caller's identity in a combination of headers, query string parameters, stageVariables, and $context variables.
API Gateway Lambda authorization workflow
- The client calls a method on an API Gateway API method, passing a bearer token (or request parameters).
- API Gateway checks whether a Lambda authorizer is configured for the method. If it is, API Gateway calls the Lambda function.
- The Lambda function authenticates the caller by means such as the following:
- Calling out to an OAuth provider to get an OAuth access token.
- Calling out to a SAML provider to get a SAML assertion.
- Generating an IAM policy based on the request parameter values.
- Retrieving credentials from a database.
- If the call succeeds, the Lambda function grants access by returning an output object containing at least an IAM policy and a principal identifier.
- API Gateway evaluates the policy.
- If access is denied, API Gateway returns a suitable HTTP status code, such as 403 ACCESS_DENIED.
- If access is allowed, API Gateway executes the method.
- If caching is enabled in the authorizer settings, API Gateway also caches the policy so that the Lambda authorizer function doesn't need to be invoked again.
Backlinks