Elastic Container Service (ECS)
running containers via AWS proprietary orchestrator
- AWS offers 2 main models for running containers: ec2 and fargate
- ECS clusters can be run a few different ways:
- run on vms
- managed docker container runtime
- EC2
- Fargate
- ECS Control Plane - The tools to manage ECS
- handles autohealing
- by default, containers behave like other Linux processes with respect to access to resources like CPU and memory. this means they get access to all of the host's CPU and memory capacity
- ecs provides mechanisms through which we can limit this (in the task)
Task
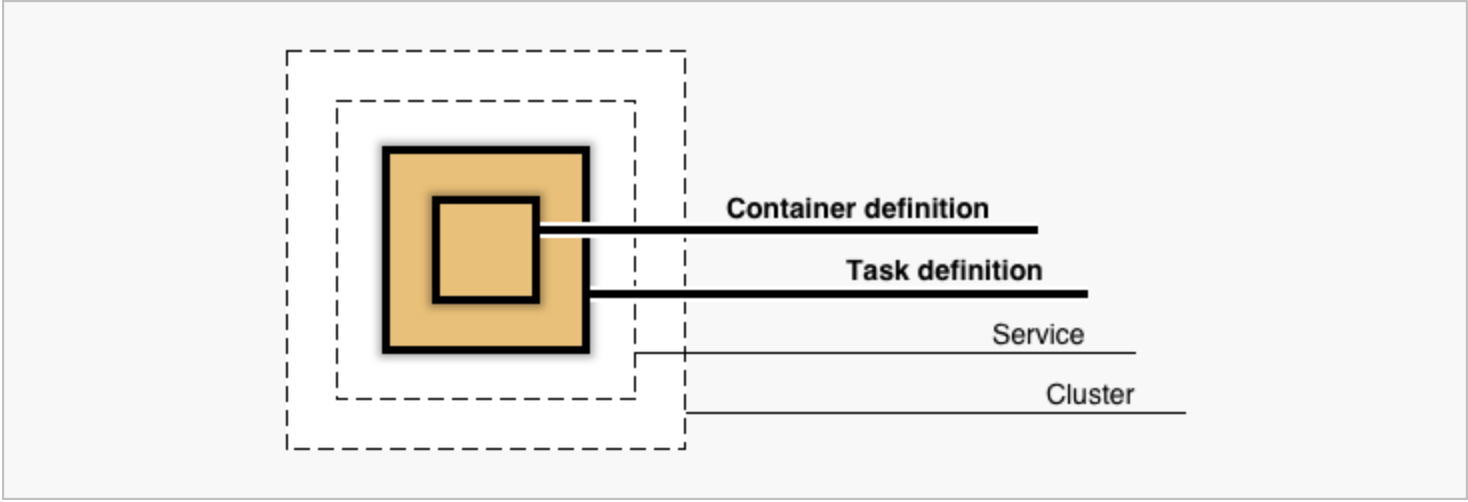
Task definition - To prepare your application to run on Amazon ECS, you create a task definition, which is a JSON file that describes between 1 and 10 containers
-
Think of it as a blueprint for your application
-
Task definition parameters might be:
- Which containers should be used?
- Which ports should be opened?
- Which data volumes should be used within the containers?
- How are container linked together
-
a
taskis an instantiation of atask definition- the basic unit of deployment is a
task
- the basic unit of deployment is a
-
a
taskis a logical construct that models 1+ containers- therefore, the ECS API operates on tasks rather than individual containers
-
in ECS you run a task, which in turn runs a container
-
each fargate task has its own isolation boundary and doesn't share kernel, cpu resources, memory resources etc
-
ECS Cluster - a regional grouping of container instances, upon which we can run task requests
- When tasks are run on Fargate, cluster resources are managed for us
- ECS cluster is a regional grouping of one or more container instances on which you can run task requests
ECS objects and how they relate
Backlinks