Oauth2
Overview
OAuth2 is an authorization framework that enables applications — such as Facebook, GitHub, and DigitalOcean — to obtain limited access to user accounts on an HTTP service
- It works by delegating user authentication to the service that hosts a user account and authorizing third-party applications to access that user account.
- OAuth2 provides authorization flows for web and desktop applications, as well as mobile devices.
OAuth defines four roles:
- Resource Owner: The resource owner is the user who authorizes an application to access their account. The application’s access to the user’s account is limited to the scope of the authorization granted (e.g. read or write access)
- Client: The client is the application that wants to access the user’s account. Before it may do so, it must be authorized by the user, and the authorization must be validated by the API.
- Resource Server: The resource server hosts the protected user accounts.
- Authorization Server: The authorization server verifies the identity of the user then issues access tokens to the application.
- From an application developer’s point of view, a service’s API fulfills both the resource and authorization server roles. We will refer to both of these roles combined, as the Service or API role.
Abstract Protocol Flow
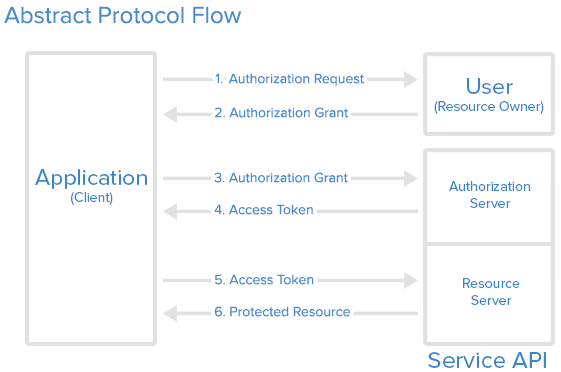
Explanation:
- The application requests authorization to access service resources from the user
- If the user authorized the request, the application receives an authorization grant
- The application requests an access token from the authorization server (API) by presenting authentication of its own identity, and the authorization grant
- If the application identity is authenticated and the authorization grant is valid, the authorization server (API) issues an access token to the application. Authorization is complete.
- The application requests the resource from the resource server (API) and presents the access token for authentication
- If the access token is valid, the resource server (API) serves the resource to the application
Application Registration
Before using OAuth with your application, you must register your application with the service (e.g. Facebook).
Once your application is registered, the service will issue client credentials in the form of a client identifier and a client secret.
-
The Client ID is a publicly exposed string that is used by the service API to identify the application. It is also used to build authorization URLs that are presented to users.
-
The Client Secret is used to authenticate the identity of the application to the service API when the application requests to access a user’s account, and must be kept private between the application and the API.
Children