Heap
Contrast with stack
- A place to store global variables.
- The heap is not automatically managed for you
- Data structure is hierarchical
- Variables need to be deallocated manually
- Garbage collection runs on the heap
- The heap is slower, but it can also store much more data than the stack
- In C,
mallocandcallocare methods used to interact with the heap. Once memory has been allocated on the heap, we must usefree()to deallocate that memory.- Failure to do this results in what’s called memory leaks.
- Pointers must be used to access memory on the heap
- allocating memory is done on the heap, not the stack (as with other variables)
- dynamic memory allocation can only be made through pointers and names (variable names) can't be given
malloc()is for allocating memory blocks from the heap in C
Heaps are used for dynamic memory allocation and unlike stacks, the program needs to look up the data in heap using pointers.
- Therefore it can store more data than a stack, but lookups take longer.
When we talk about "memory management" we are mostly talking about managing the Heap memory.
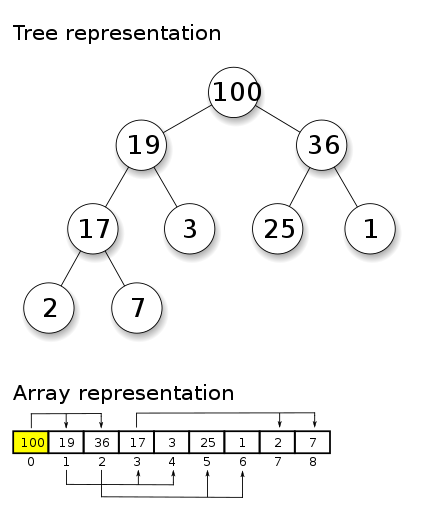
A heap is a tree structure
Backlinks