Sliding Window
Big O
- Time Complexity - The time complexity of this pattern is
0(N) - Space Complexity - The algorithm runs in constant space
O(1)
Recognizing Sliding Window Problems
- when the problem has us finding the mix, max, longest, shortest
- we are looking at subarrays within the array
Example: Calculate averages
This function takes in an array, and sums the first k elements, computes its average then sticks it in the array. Then it sums the next k elements, computes average, adds to an array, and so on until the end of the array. Consider that we could brute-force this by having each iteration take a sum then average of each k sized window. However this has a major inefficiency, which is that the same elements are counted multiple times needlessly.
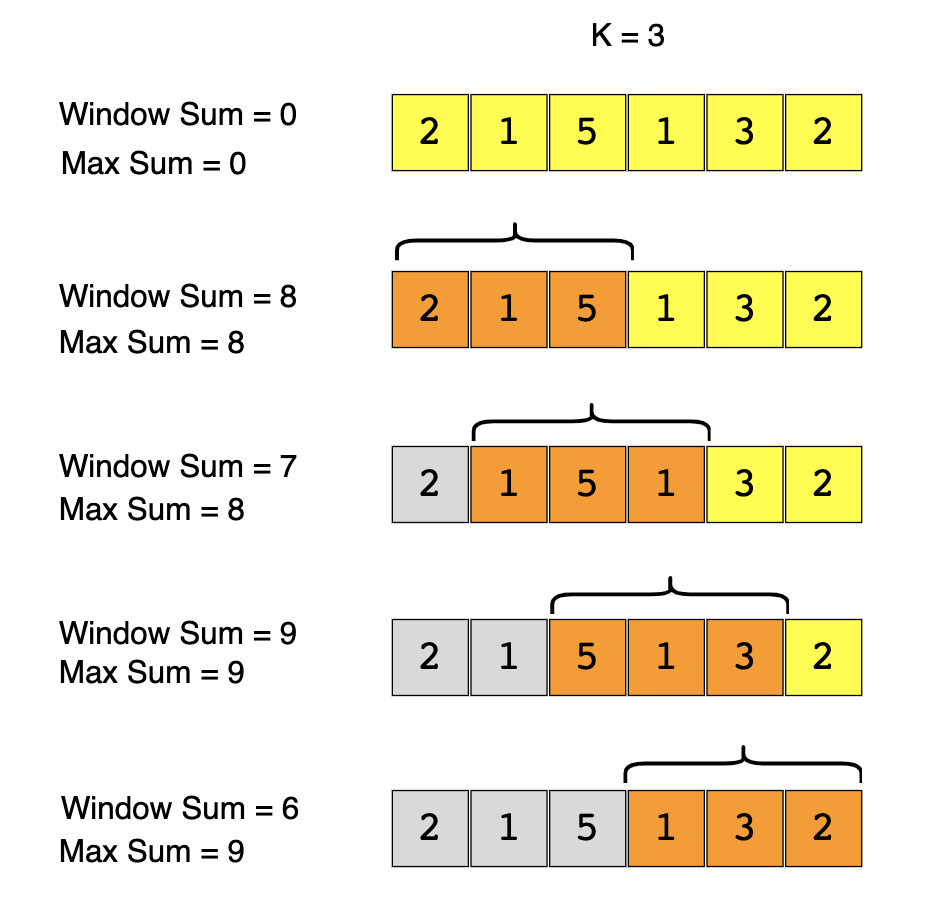
Instead, our approach here lets us leverage previously summed up numbers by simply removing the start of the window (frontIndex) and adding the end of the window (backIndex) on each iteration.
const calculateAverages = (arr, size) => {
let backIndex = size - 1
let frontIndex = 0
const averageResults = []
let sum = arr
.slice(frontIndex, backIndex + 1)
.reduce((acc, val) => acc + val)
while (backIndex < arr.length) {
averageResults.push(sum / size)
// remove the front of the window, and add the back of the window
sum = sum - arr[frontIndex] + arr[backIndex + 1]
frontIndex++
backIndex++
}
return averageResults
}
const arr = [1, 3, 2, 6, -1, 4, 1, 8, 2]
const k = 5
const averages = calculateAverages(arr, k)
// [ 2.2, 2.8, 2.4, 3.6, 2.8]
Resources
Backlinks