Data Warehouse
A data warehouse is a database optimized to analyze relational data coming from transactional systems and line of business applications.
Data is transferred into the warehouse via an ETL pipeline using either a periodic data dump (ie. a batch) or a continuous stream of updates.
The data model of a data warehouse is most commonly relational, because SQL is generally a good fit for analytic queries.
The data structure, and schema are defined in advance to optimize for fast SQL queries, where the results are typically used for operational reporting and analysis.
- Data is cleaned, enriched, and transformed so it can act as the “single source of truth” that users can trust.
It differs from a Lake because it stores the data in a single format, whereas a data lake stores the data as-is (Postgres, Mongo etc.)
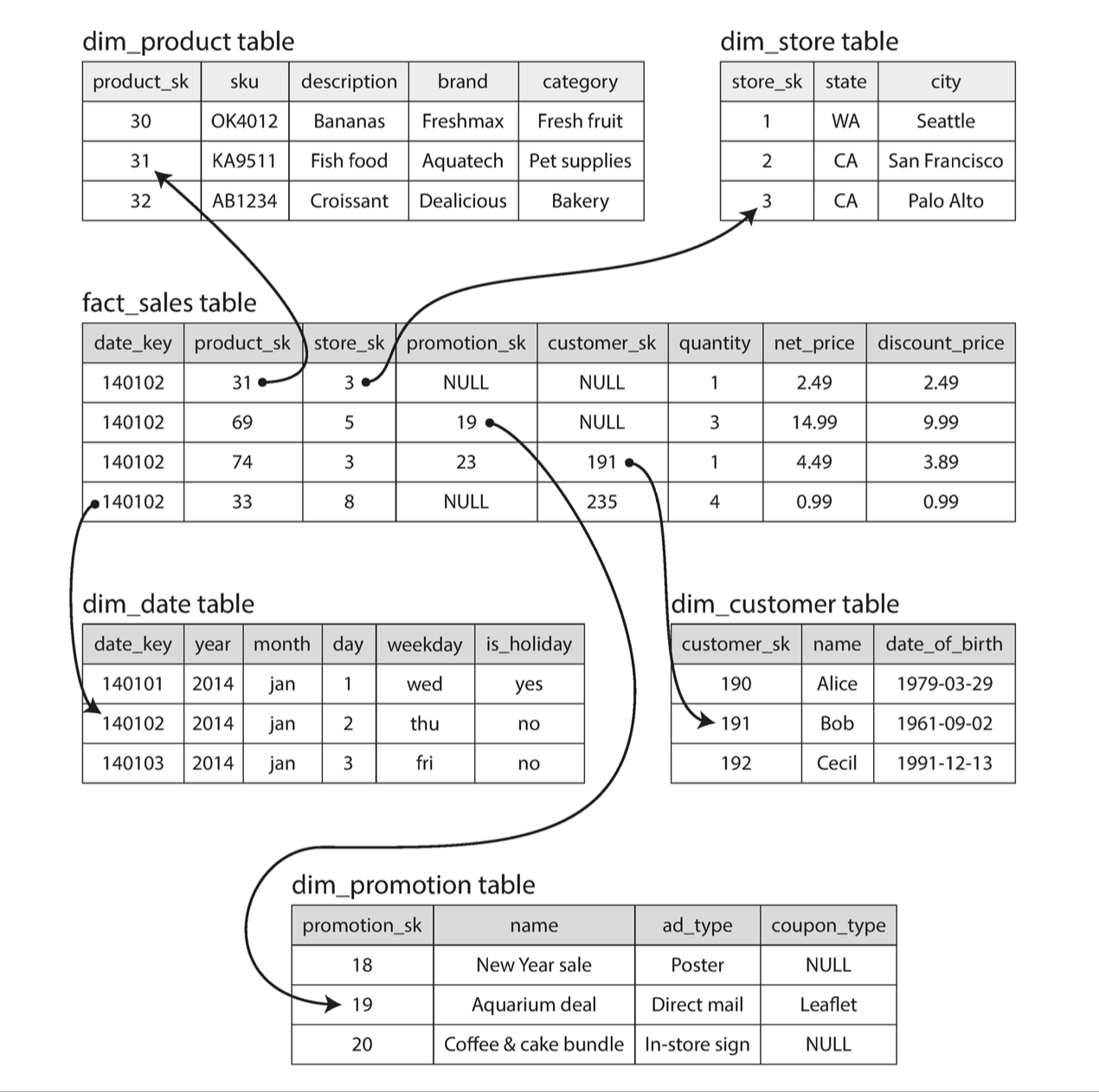
Star schema
When it comes to data analytics, there is much less diversity of data models. Many data warehouses are used in a fairly formulaic style, known as a star schema (a.k.a dimensional modeling)
Usually, facts are captured as individual events, because this allows maximum flexi‐ bility of analysis later.
- as a result, fact tables are massive. A company like Walmart would have tens of petabytes of data in a fact table.
Other tables that "feed into" the fact table are known as dimension tables.
- If each row in the fact table represents an event, the dimensions represent the who, what, where, when, how, and why of the event.
Backlinks